16 KiB
| date | title | weight |
|---|---|---|
| 2016-04-09T16:50:16+02:00 | Syntaxe Markdown | 15 |
{{% notice note %}} Cette page est une copie de la doc de Grav. La seule différence porte sur la personalisation des images ([taille]({{< relref "#resizing-image" >}}), [ajout de classes CSS]({{< relref "#add-css-classes" >}})...) Pour des raisons évidentes, cette page n'a pas été traduites en français 😁 {{% /notice%}}
Let's face it: Writing content for the Web is tiresome. WYSIWYG editors help alleviate this task, but they generally result in horrible code, or worse yet, ugly web pages.
Markdown is a better way to write HTML, without all the complexities and ugliness that usually accompanies it.
Some of the key benefits are:
- Markdown is simple to learn, with minimal extra characters so it's also quicker to write content.
- Less chance of errors when writing in markdown.
- Produces valid XHTML output.
- Keeps the content and the visual display separate, so you cannot mess up the look of your site.
- Write in any text editor or Markdown application you like.
- Markdown is a joy to use!
John Gruber, the author of Markdown, puts it like this:
The overriding design goal for Markdown’s formatting syntax is to make it as readable as possible. The idea is that a Markdown-formatted document should be publishable as-is, as plain text, without looking like it’s been marked up with tags or formatting instructions. While Markdown’s syntax has been influenced by several existing text-to-HTML filters, the single biggest source of inspiration for Markdown’s syntax is the format of plain text email. -- John Gruber
Grav ships with built-in support for Markdown and Markdown Extra. You must enable Markdown Extra in your system.yaml configuration file
Without further delay, let us go over the main elements of Markdown and what the resulting HTML looks like:
{{% notice info %}} Bookmark this page for easy future reference! {{% /notice %}}
Headings
Headings from h1 through h6 are constructed with a # for each level:
# h1 Heading
## h2 Heading
### h3 Heading
#### h4 Heading
##### h5 Heading
###### h6 Heading
Renders to:
h1 Heading
h2 Heading
h3 Heading
h4 Heading
h5 Heading
h6 Heading
HTML:
<h1>h1 Heading</h1>
<h2>h2 Heading</h2>
<h3>h3 Heading</h3>
<h4>h4 Heading</h4>
<h5>h5 Heading</h5>
<h6>h6 Heading</h6>
Comments
Comments should be HTML compatible
<!--
This is a comment
-->
Comment below should NOT be seen:
Horizontal Rules
The HTML <hr> element is for creating a "thematic break" between paragraph-level elements. In markdown, you can create a <hr> with any of the following:
___: three consecutive underscores---: three consecutive dashes***: three consecutive asterisks
renders to:
Body Copy
Body copy written as normal, plain text will be wrapped with <p></p> tags in the rendered HTML.
So this body copy:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, graecis denique ei vel, at duo primis mandamus. Et legere ocurreret pri, animal tacimates complectitur ad cum. Cu eum inermis inimicus efficiendi. Labore officiis his ex, soluta officiis concludaturque ei qui, vide sensibus vim ad.
renders to this HTML:
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, graecis denique ei vel, at duo primis mandamus. Et legere ocurreret pri, animal tacimates complectitur ad cum. Cu eum inermis inimicus efficiendi. Labore officiis his ex, soluta officiis concludaturque ei qui, vide sensibus vim ad.</p>
Emphasis
Bold
For emphasizing a snippet of text with a heavier font-weight.
The following snippet of text is rendered as bold text.
**rendered as bold text**
renders to:
rendered as bold text
and this HTML
<strong>rendered as bold text</strong>
Italics
For emphasizing a snippet of text with italics.
The following snippet of text is rendered as italicized text.
_rendered as italicized text_
renders to:
rendered as italicized text
and this HTML:
<em>rendered as italicized text</em>
strikethrough
In GFM (GitHub flavored Markdown) you can do strikethroughs.
~~Strike through this text.~~
Which renders to:
Strike through this text.
HTML:
<del>Strike through this text.</del>
Blockquotes
For quoting blocks of content from another source within your document.
Add > before any text you want to quote.
> **Fusion Drive** combines a hard drive with a flash storage (solid-state drive) and presents it as a single logical volume with the space of both drives combined.
Renders to:
Fusion Drive combines a hard drive with a flash storage (solid-state drive) and presents it as a single logical volume with the space of both drives combined.
and this HTML:
<blockquote>
<p><strong>Fusion Drive</strong> combines a hard drive with a flash storage (solid-state drive) and presents it as a single logical volume with the space of both drives combined.</p>
</blockquote>
Blockquotes can also be nested:
> Donec massa lacus, ultricies a ullamcorper in, fermentum sed augue.
Nunc augue augue, aliquam non hendrerit ac, commodo vel nisi.
>> Sed adipiscing elit vitae augue consectetur a gravida nunc vehicula. Donec auctor
odio non est accumsan facilisis. Aliquam id turpis in dolor tincidunt mollis ac eu diam.
Renders to:
Donec massa lacus, ultricies a ullamcorper in, fermentum sed augue. Nunc augue augue, aliquam non hendrerit ac, commodo vel nisi.
Sed adipiscing elit vitae augue consectetur a gravida nunc vehicula. Donec auctor odio non est accumsan facilisis. Aliquam id turpis in dolor tincidunt mollis ac eu diam.
Notices
{{% notice note %}}
The old mechanism for notices overriding the block quote syntax (>>>) has been deprecated. Notices are now handled via a dedicated plugin called Markdown Notices
{{% /notice %}}
Lists
Unordered
A list of items in which the order of the items does not explicitly matter.
You may use any of the following symbols to denote bullets for each list item:
* valid bullet
- valid bullet
+ valid bullet
For example
+ Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
+ Consectetur adipiscing elit
+ Integer molestie lorem at massa
+ Facilisis in pretium nisl aliquet
+ Nulla volutpat aliquam velit
- Phasellus iaculis neque
- Purus sodales ultricies
- Vestibulum laoreet porttitor sem
- Ac tristique libero volutpat at
+ Faucibus porta lacus fringilla vel
+ Aenean sit amet erat nunc
+ Eget porttitor lorem
Renders to:
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
- Consectetur adipiscing elit
- Integer molestie lorem at massa
- Facilisis in pretium nisl aliquet
- Nulla volutpat aliquam velit
- Phasellus iaculis neque
- Purus sodales ultricies
- Vestibulum laoreet porttitor sem
- Ac tristique libero volutpat at
- Faucibus porta lacus fringilla vel
- Aenean sit amet erat nunc
- Eget porttitor lorem
And this HTML
<ul>
<li>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet</li>
<li>Consectetur adipiscing elit</li>
<li>Integer molestie lorem at massa</li>
<li>Facilisis in pretium nisl aliquet</li>
<li>Nulla volutpat aliquam velit
<ul>
<li>Phasellus iaculis neque</li>
<li>Purus sodales ultricies</li>
<li>Vestibulum laoreet porttitor sem</li>
<li>Ac tristique libero volutpat at</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>Faucibus porta lacus fringilla vel</li>
<li>Aenean sit amet erat nunc</li>
<li>Eget porttitor lorem</li>
</ul>
Ordered
A list of items in which the order of items does explicitly matter.
1. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
2. Consectetur adipiscing elit
3. Integer molestie lorem at massa
4. Facilisis in pretium nisl aliquet
5. Nulla volutpat aliquam velit
6. Faucibus porta lacus fringilla vel
7. Aenean sit amet erat nunc
8. Eget porttitor lorem
Renders to:
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
- Consectetur adipiscing elit
- Integer molestie lorem at massa
- Facilisis in pretium nisl aliquet
- Nulla volutpat aliquam velit
- Faucibus porta lacus fringilla vel
- Aenean sit amet erat nunc
- Eget porttitor lorem
And this HTML:
<ol>
<li>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet</li>
<li>Consectetur adipiscing elit</li>
<li>Integer molestie lorem at massa</li>
<li>Facilisis in pretium nisl aliquet</li>
<li>Nulla volutpat aliquam velit</li>
<li>Faucibus porta lacus fringilla vel</li>
<li>Aenean sit amet erat nunc</li>
<li>Eget porttitor lorem</li>
</ol>
TIP: If you just use 1. for each number, Markdown will automatically number each item. For example:
1. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
1. Consectetur adipiscing elit
1. Integer molestie lorem at massa
1. Facilisis in pretium nisl aliquet
1. Nulla volutpat aliquam velit
1. Faucibus porta lacus fringilla vel
1. Aenean sit amet erat nunc
1. Eget porttitor lorem
Renders to:
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
- Consectetur adipiscing elit
- Integer molestie lorem at massa
- Facilisis in pretium nisl aliquet
- Nulla volutpat aliquam velit
- Faucibus porta lacus fringilla vel
- Aenean sit amet erat nunc
- Eget porttitor lorem
Code
Inline code
Wrap inline snippets of code with `.
In this example, `<section></section>` should be wrapped as **code**.
Renders to:
In this example, <section></section> should be wrapped with code.
HTML:
<p>In this example, <code><section></section></code> should be wrapped with <strong>code</strong>.</p>
Indented code
Or indent several lines of code by at least four spaces, as in:
// Some comments line 1 of code line 2 of code line 3 of code
Renders to:
// Some comments
line 1 of code
line 2 of code
line 3 of code
HTML:
<pre>
<code>
// Some comments
line 1 of code
line 2 of code
line 3 of code
</code>
</pre>
Block code "fences"
Use "fences" ``` to block in multiple lines of code.
``` markup Sample text here... ```
Sample text here...
HTML:
<pre>
<code>Sample text here...</code>
</pre>
Syntax highlighting
GFM, or "GitHub Flavored Markdown" also supports syntax highlighting. To activate it, simply add the file extension of the language you want to use directly after the first code "fence", ```js, and syntax highlighting will automatically be applied in the rendered HTML. For example, to apply syntax highlighting to JavaScript code:
```js
grunt.initConfig({
assemble: {
options: {
assets: 'docs/assets',
data: 'src/data/*.{json,yml}',
helpers: 'src/custom-helpers.js',
partials: ['src/partials/**/*.{hbs,md}']
},
pages: {
options: {
layout: 'default.hbs'
},
files: {
'./': ['src/templates/pages/index.hbs']
}
}
}
};
```
Renders to:
grunt.initConfig({
assemble: {
options: {
assets: 'docs/assets',
data: 'src/data/*.{json,yml}',
helpers: 'src/custom-helpers.js',
partials: ['src/partials/**/*.{hbs,md}']
},
pages: {
options: {
layout: 'default.hbs'
},
files: {
'./': ['src/templates/pages/index.hbs']
}
}
}
};
Tables
Tables are created by adding pipes as dividers between each cell, and by adding a line of dashes (also separated by bars) beneath the header. Note that the pipes do not need to be vertically aligned.
| Option | Description |
| ------ | ----------- |
| data | path to data files to supply the data that will be passed into templates. |
| engine | engine to be used for processing templates. Handlebars is the default. |
| ext | extension to be used for dest files. |
Renders to:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| data | path to data files to supply the data that will be passed into templates. |
| engine | engine to be used for processing templates. Handlebars is the default. |
| ext | extension to be used for dest files. |
And this HTML:
<table>
<tr>
<th>Option</th>
<th>Description</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>data</td>
<td>path to data files to supply the data that will be passed into templates.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>engine</td>
<td>engine to be used for processing templates. Handlebars is the default.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>ext</td>
<td>extension to be used for dest files.</td>
</tr>
</table>
Right aligned text
Adding a colon on the right side of the dashes below any heading will right align text for that column.
| Option | Description |
| ------:| -----------:|
| data | path to data files to supply the data that will be passed into templates. |
| engine | engine to be used for processing templates. Handlebars is the default. |
| ext | extension to be used for dest files. |
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| data | path to data files to supply the data that will be passed into templates. |
| engine | engine to be used for processing templates. Handlebars is the default. |
| ext | extension to be used for dest files. |
Links
Basic link
[Assemble](http://assemble.io)
Renders to (hover over the link, there is no tooltip):
HTML:
<a href="http://assemble.io">Assemble</a>
Add a title
[Upstage](https://github.com/upstage/ "Visit Upstage!")
Renders to (hover over the link, there should be a tooltip):
HTML:
<a href="https://github.com/upstage/" title="Visit Upstage!">Upstage</a>
Named Anchors
Named anchors enable you to jump to the specified anchor point on the same page. For example, each of these chapters:
# Table of Contents
* [Chapter 1](#chapter-1)
* [Chapter 2](#chapter-2)
* [Chapter 3](#chapter-3)
will jump to these sections:
## Chapter 1 <a id="chapter-1"></a>
Content for chapter one.
## Chapter 2 <a id="chapter-2"></a>
Content for chapter one.
## Chapter 3 <a id="chapter-3"></a>
Content for chapter one.
NOTE that specific placement of the anchor tag seems to be arbitrary. They are placed inline here since it seems to be unobtrusive, and it works.
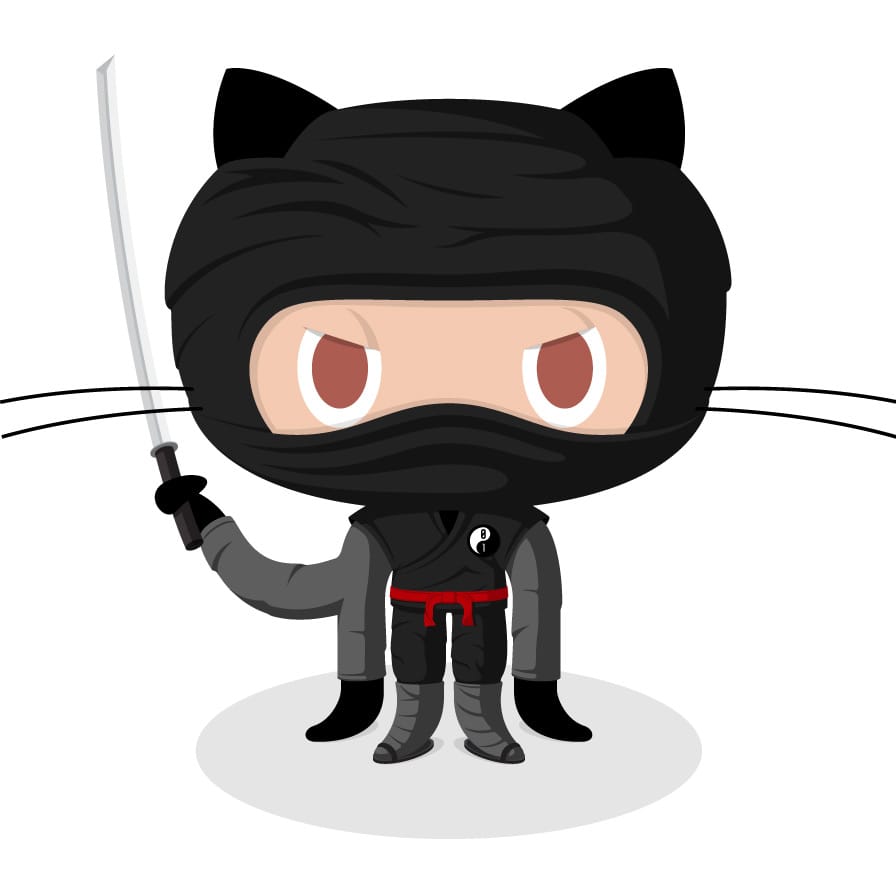
Images
Images have a similar syntax to links but include a preceding exclamation point.

or

Like links, Images also have a footnote style syntax
Alternative usage : note images
![Alt text][id]
With a reference later in the document defining the URL location:
[id]: https://octodex.github.com/images/dojocat.jpg "The Dojocat"
Resizing image
Add HTTP parameters width and/or height to the link image to resize the image. Values are CSS values (default is auto).
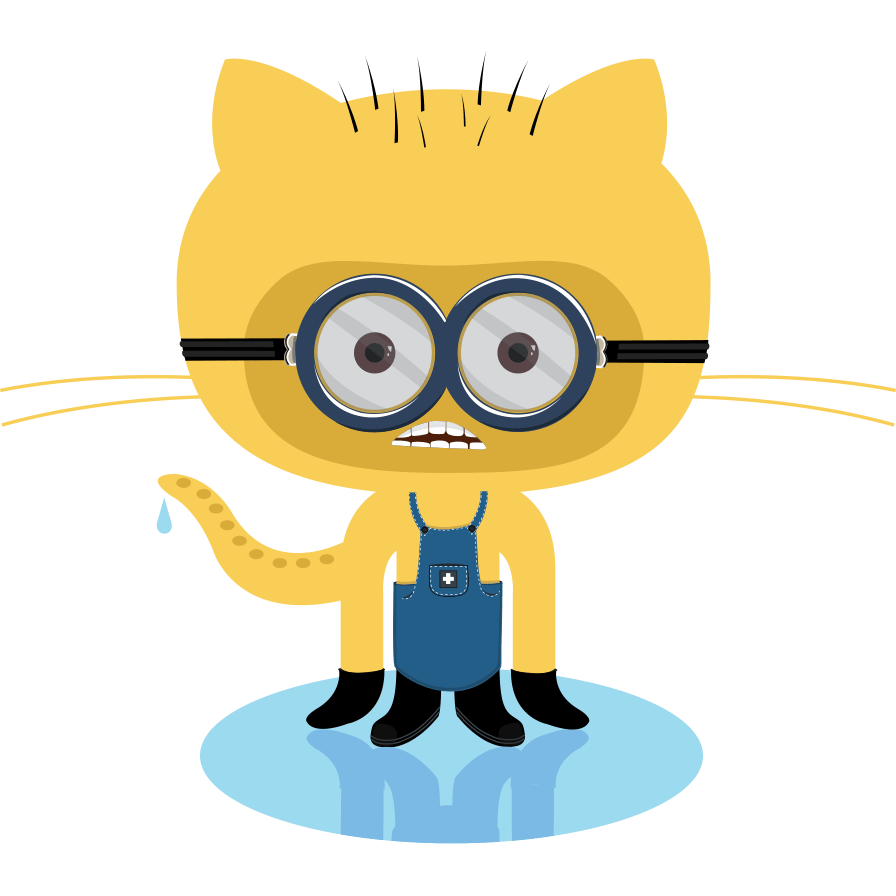
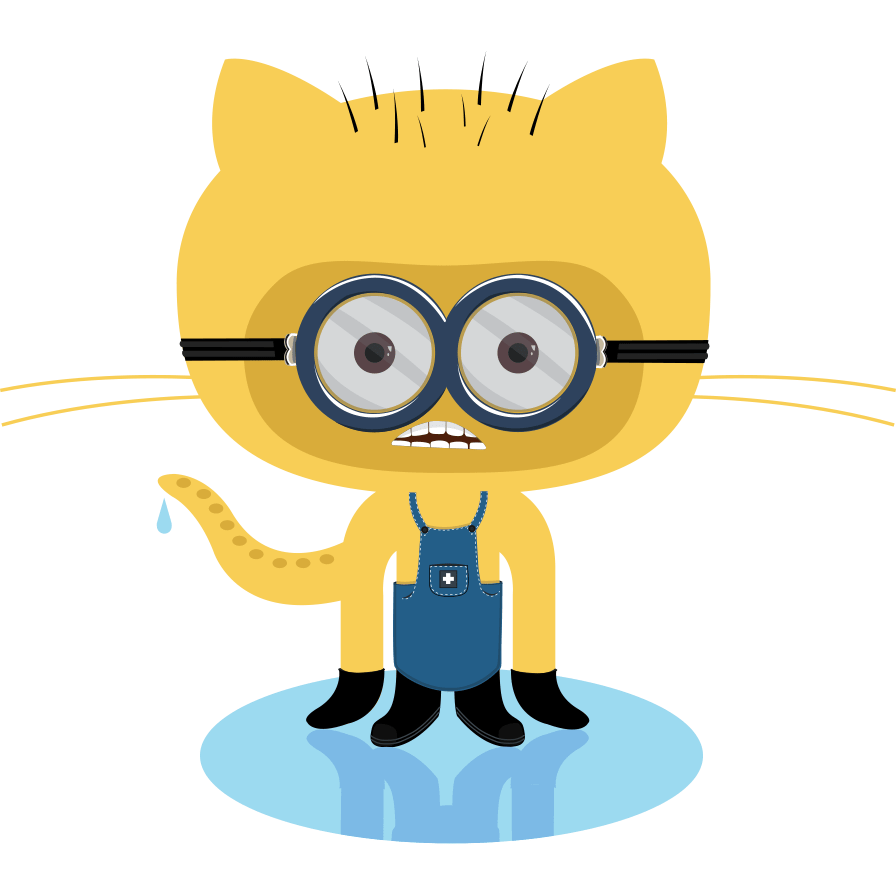
Add CSS classes
Add a HTTP classes parameter to the link image to add CSS classes. shadowand border are available but you could define other ones.